A relay may be used in circuits where it is not possible to have a direct electrical connection between the control circuit and the output device: eg due to the risk of damage to the circuit from back electromotive force (EMF).
A relay is a special type of switch turned on and off by an electromagnet (see the diagram of a simple relay). When a current flows through the coil an electro-magnetic field is set up. The field attracts an iron armature, whose other end pushes the contacts together, completing the circuit. When the current is switched off, the contacts open again, switching the circuit off.
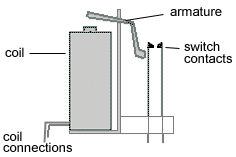
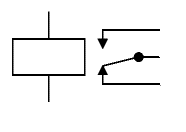
A useful property of relays is that the circuit powering the coil is completely separate from the circuit switched on by the relay. For this reason relays are used where a safe low-voltage circuit controls a high-voltage circuit.
The symbol for a relay makes the separation of the two circuits clear by separating the coil symbol from the switch symbol.
The relays used in schools generally have a voltage between 6V and 15V. When using a diode with a relay, be sure that it is connected across the poles (terminals) of the relay to prevent damage to the transistor from back EMF, generated when the relay coil switches off
Copyright:@2020-2021
Comments Please sign in or sign up to post.
0
0 of 500 characters used