AI and robotics are two tech industry buzzwords as common as computers. Every company and product has seemed to innovate their offerings with AI in some fashion, so why shouldn’t solar follow suit?
Solar energy installations have grown tremendously over the last decade with no signs of slowing down. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), photovoltaic solar accounted for 67% of all new electric generating capacity in the US – up from only 25% ten years ago in 2014.
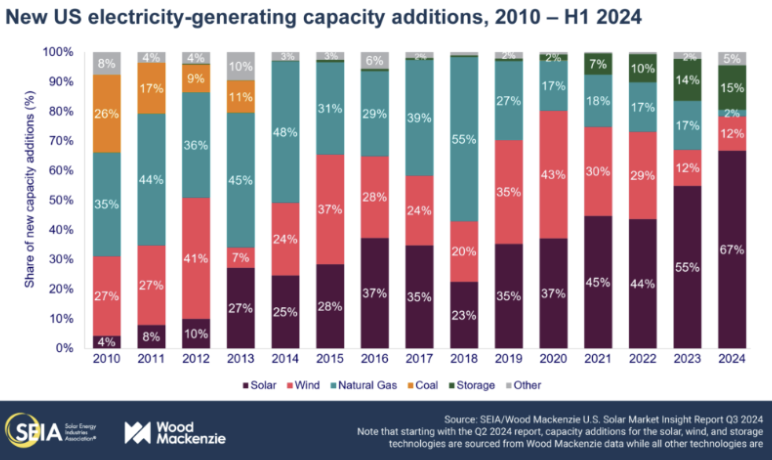
Commercial and Utility-scale solar installations are driving the vast majority of that growth. The above report notes that as of Q3 2024, this is how each segment stands:
Residential Solar: 1,132 MW DC installed in Q2 2024, down 37% from Q2 2023
Commercial Solar: 427 MW DC installed in Q2 2024, up 6% from Q2 2023
Community Solar: 270 MW DC installed in Q2 2024, down 12% from Q2 2023
Utility Solar: 5 GW DC installed in Q2 2024, up 59% from Q2 2023
Large-scale solar deployment is seeing major gains because utilities continue investing in the lowest cost and safest forms of electricity, solar and wind. SEIA also notes that pricing for commercial systems is down 12% year over year and utility-scale system pricing is down 2% for fixed tilt and 1% for single-axis tracking.
Unsurprisingly, the continued growth of commercial and utility-scale PV is leading to more investment and innovation in the segment, some of which have the potential to blow the doors off the projections for deployment.
The use of robotics in solar energy is rapidly transforming the industry and providing solutions that increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety. Robotics have been used for some time in solar module manufacturing to speed up manufacturing processes and remove human error, similar to how to the automotive industry has adopted robotics and automation.
With the explosion in commercial and industrial-scale solar, robotics and automation have begun making their way into the field. Traditionally, installing and maintaining solar farms requires significant labor, with tasks such as panel positioning, cleaning, and inspection being performed manually. However, robotics has started to streamline these processes by automating time-consuming activities.
One of the most significant limiting factors of solar installation is having manpower at the site. Large-scale solar developments require crews to work long hours lifting heavy modules for weeks to months to survey and prep the site, let alone the additional time it takes to build the systems on-site.
These robotic advancements, coupled with AI and computer vision are pushing the boundaries of solar development, simplifying solar installation and operations alike.
On top of the mechanical and personal benefits, utilizing technology like the above gives unprecedented analytical looks at a construction site. Unlike traditional construction crews, an installation site with robotics and AI would be able to give management more predictable installation timelines. and allow them to deploy resources more efficiently.
With continued development and demand, we may soon see a world where commercial and industrial-scale solar is deployed with minimal human interaction and at fractions of the cost seen today.
For more details please conatct www.trinarobot.com
Previous: Exploring the Benefits of Crawler Scissor Lifts
Next: How Long Does a Crusher Last? – Understanding the Lifespan and Key Factors
Copyright:@2020-2021
Comments Please sign in or sign up to post.
0
0 of 500 characters used