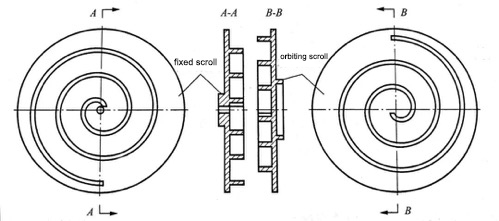
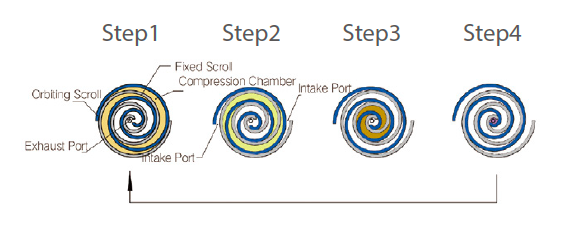
The pumping process of the scroll vacuum pump is realized by the meshing motion of the movable scroll and the stationary scroll at all times. Therefore, the design of the scroll is one of the important steps in the development of the scroll vacuum pump, which determines the suction of the scroll vacuum pump. The most important design of the scroll is the design of the scroll profile. In general, the scroll profile of the orbiting scroll and the fixed scroll is the same.
Scroll vacuum pump types and structure
Scroll vacuum pumps can be divided into two types according to the different scroll motion modes, revolution type, and rotary type. One scroll of the pump is fixed and is called a fixed scroll, and the other scroll is an orbiting scroll. The motor drives the crankshaft to rotate, and the crankshaft pushes the center of the base circle of the movable scroll around the base circle of the stationary scroll to make a circular motion of radius r. The anti-rotation structure restricts the movable scroll from rotating.
The two scrolls in the rotary scroll vacuum pump are movable scrolls, and they rotate in the same direction around their own base circle center.
a. Revolution type
The revolution-type scroll vacuum pump is one scroll that is stationary (fixed scroll) and the other that revolves around it and translates (orbiting scroll). The crankshaft drives the orbiting scroll, and the position of the sealing point rotates synchronously with the main shaft. It has a simple overall structure and few parts. The rotary speed of the vortex is small, and the mechanical wear is small, but it needs a dynamic balance design. The scroll vacuum pump uses the outermost scroll ring to contain gas to form a closed suction chamber. In order to reduce the flow conductance between the scroll and the air inlet, the air inlet is set near the end of the outer ring of the scroll. The port is located near the center of the stationary scroll.
b. Rotary type
The rotary-type scroll vacuum pump consists of two scrolls mounted on the bearings on both sides, one of which is directly driven by a motor, and the other is driven by a cross-slip ring mechanism to rotate in the same direction. Its sealing position forms a line, the direction is always the same, and the pump adopts a vertical structure. The drive motor is in the upper part of the casing, and the scroll is in the lower part. Its overall structure is complex, with many parts and high mechanical wear.
c. Difference between two types
◆Different way of turning
◆Different seal positions and orientations
◆The direction of the gas radial and tangential forces on the scroll is different
◆Different balance
◆Overturning torque and axial force are different
Scroll vacuum pump vacuum range
The vacuum range of a scroll vacuum pump refers to the range of pressures that the pump is capable of achieving and maintaining. The vacuum range is determined by the pump's design, construction, and operating conditions.
Scroll vacuum pumps can work from atmospheric pressure. The ultimate vacuum of different brands of scroll vacuum pumps is different, but usually, it can reach 10Pa to 0.5Pa. However, it is important to note that the vacuum range of a scroll vacuum pump can vary depending on factors such as the size of the pump, the type of scroll pump, and the operating conditions (temperature, oil-free operation, etc.). Additionally, the vacuum range can be affected by factors such as leaks, blockages, or contaminants in the pump or the vacuum system.
Features of scroll vacuum pumps
◆ Small gap, less leakage, and high vacuum degree.
◆ Simple structure and few parts.
◆ The working pressure range is wide. Because the volume of the working chamber changes continuously, the change in driving torque and power is small.
◆ Low vibration noise and high reliability.
◆ Due to the limitation of its own characteristics, the scroll vacuum pump is not easy to make into a pump with a large pumping rate. At present, the pumping rate of the scroll vacuum pump of some manufacturers can reach 16L/s.
Application of oil-free scroll vacuum pumps
◆Semiconductor industry - thin film preparation equipment, semiconductor packaging equipment;
◆Scientific instrument industry - synchrotron radiation beamlines, electron microscopes, analysis, and testing instruments;
◆Mechanical equipment industry - material preparation equipment, vacuum testing, material purification equipment;
◆Chemical industry;
◆Medical equipment - dental instruments, dialysis machines, biological products, and drug preparation;
◆ Packaging industry - packaging equipment for food, medicine, biological products, etc.


Comments Please sign in or sign up to post.
0
0 of 500 characters used