Bridge bearing is a critical component, it provides a bridge with flexibility, and it is used to transfer the loads from superstructure to substructure.
● Facilitate transfer of vehicular and other environmentally imposed loads from the superstructure to the substructure.
● Accommodate anticipated movements such as thermal, shrinkage, creep movement.
Elastomeric bearings are made of layers of synthetic chloroprene rubber (CR) or natural rubber (NR). Steel plates are placed between rubber layers, rubber layer will be merged by vulcanization to produce a single pad. The elastomeric bearing will allow for rotation of superstructure. Movement of the superstructure will be accommodated through elastic deformation.

Figure 1
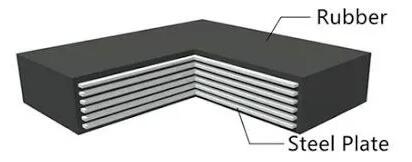
Figure 2
In the beginning, bridges have been built with materials like stone or timber. The nature of those structures made it possible to place them directly into the supporting elements or even the soil itself. Furthermore, there was not the awareness and the knowledge about structural seismic performance that we have today. With new and specialized materials and the need to protect the structures from events like earthquakes, structural bearings have begun, and there are currently many options for different types of bridges.
Of all structural bearings, elastomeric bearings are frequently used elements to support concrete superstructures and transmit the loads to the substructures. This type of bearings has also shown adequate behavior in other types of materials and types of structures.
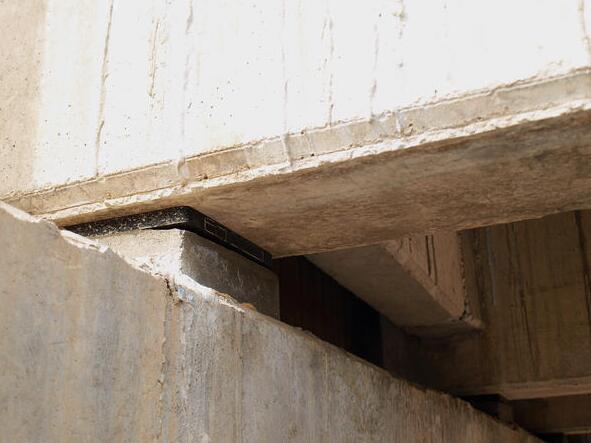

Figure 3. Elastomeric bearing pad in a concrete bridge
The design of elastomeric bearings deals with the equilibrium between having sufficient stiffness that can withstand the imposed vertical loads and enough flexibility to allow for the expected deformations. The stiffness and flexibility requirements are well enhanced with the use of steel plates and rubber, respectively. Then, elastomeric bearings can either be plain or reinforced with internal steel plates.

Figure 4. Plain (left) and reinforced (right) elastomeric bearing pads
As reference values for proper use, reinforced elastomeric bearings can usually be used for (vertical) loads up to 3500 kN, translations up to 100 mm, rotations up to 0,04 radians (for typical bending behavior), and have a low initial and maintenance cost (AISI and NSBA, 1996).
Pot bearing consist of a steel pot, the steel pot enclosing an elastomeric disc, the elastomeric disk pressed from the top by a steel plate, elastomeric will act as a viscous material and the top plate as a piston, pot bearing can accommodate a sizeable compressive force, pot bearing divided into:
● Fixed pot bearing: fixed bearing will allow rotation only with no movement
● Guided pot bearing: guided bearing will allow rotation with translation movement in one direction only, sliding material with low friction coefficient(usually PTFE) will be used and slide against hard mat typically stainless steel, a guided bar will be used to restrict movement in other direction
● Free pot bearing: free pot bearing will allow rotation and translation movement in both directions.
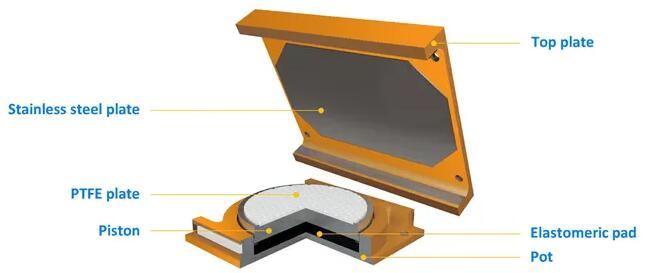
Figure 5

Figure 6
It is recommended to use pot bearing for high vertical load combined with a large angle of rotation. Using elastomeric bearing under these conditions will require a large surface bearing area so the compression can be transferred from the superstructure to piers. This can result in uneven stress distribution and damage to the substructure.

Previous: SLIDING VS STACKER DOORS
Next: U FENCE POST
Copyright:@2020-2021
Comments Please sign in or sign up to post.
0
0 of 500 characters used