A: Solubility in water
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is actually a methyl cellulose modified by propylene oxide (methyl oxypropylene), so it still has the characteristics of cold water solubility and hot water insolubility similar to methyl cellulose. However, due to the modified hydroxypropyl group, its gelation temperature in hot water is much higher than that of methyl cellulose.
B: Solubility in organic solvents
High-viscosity hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose with a total degree of substitution above 1.8 is soluble in anhydrous methanol and ethanol solutions and is thermoplastic and water-soluble. It is also soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform, and in organic solvents such as acetone, isopropanol, and diacetone alcohol. Its solubility in organic solvents is better than water-soluble.

A: Standard viscosity measurement, which is the standard measurement in 2% aqueous solution at 20°C. The viscosity of the same product increases with the increase of concentration. For products with different molecular weights at the same concentration, the products with larger molecular weights have higher viscosity.
B: The viscosity and temperature relationship are that when the temperature increases, the viscosity begins to decrease, but when the temperature reaches a certain temperature, the viscosity suddenly increases and gelation occurs.

Since hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is a non-ionic ether, it is not ionized in the medium of water. General salts such as chloride, bromide, phosphate, nitrate, etc. are added to its aqueous solution without precipitation. However, the addition of salts has some influence on the flocculation temperature of its aqueous solution. When the salt concentration increases, the gel temperature decreases. When the salt concentration is below the flocculation point, the viscosity of the solution tends to increase. Therefore, in the application, adding a certain amount of salt can achieve the thickening effect more economically.

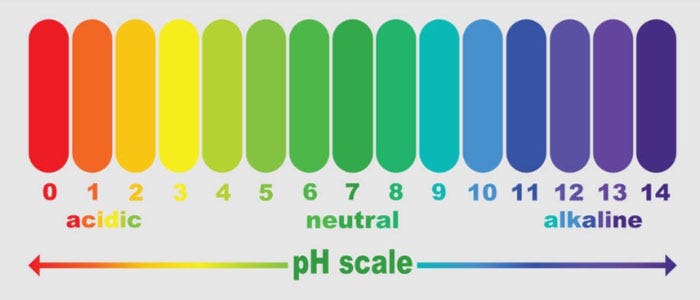
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is generally stable to acid and alkali, and is not affected in the range of pH2~12. It can withstand a certain amount of light acid, but concentrated acid has the effect of reducing viscosity. Alkali such as caustic soda, caustic potash, and lime water has no effect on it, but it can slightly increase the viscosity of the solution, and then there will be a phenomenon of a slow decline in the future.
Copyright:@2020-2021
Comments Please sign in or sign up to post.
0
0 of 500 characters used